Reaction Coordinate Diagram E1, Elimination Reactions Ppt Video Online Download
- Dehydration Of Alcohols By E1 And E2 Elimination With Practice Problems Chemistry Steps
- 8 5 Elimination Reactions Chemistry Libretexts
- Http Anslyn Cm Utexas Edu Courses Physorg Fall2019 Exams Files 2016 Exam3 Key Pdf
- Figure 3 Energies Of Competing Sn1 And E1 Reactions In Comparison Learning To Think In Mechanistic Alternatives Sn1 Vs E1 And The Gibbs Helmholtz Equation Science And Education Publishing
- 2
- 1
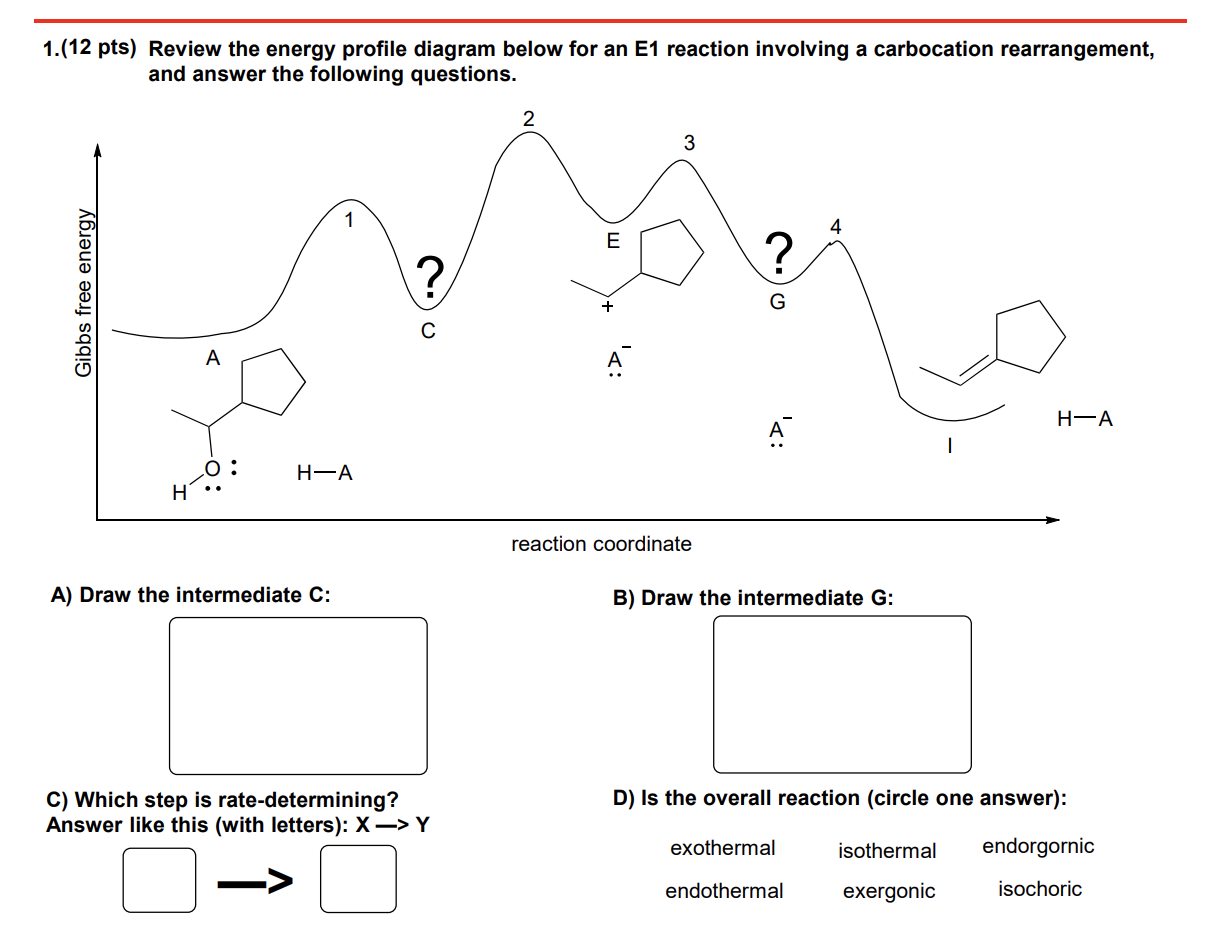
- Draw A Reaction Profile Diagram Of Energy Vs Reaction Coordinate For A Hypothetical Reaction Ab C Arrow A Bc In Which The Foward Reaction Has An Activation Energy Of 100
- 1 Synthesize A Molecule By Using An Reagent You Can Think Of There Should Be The Following Reactions Sn2 E2 Sn1 E1 Homeworklib
- What Is The Difference Between A Transition State And An Intermediate Organic Chemistry Tutor
- Chapter 8 Lecture Powerpoint Ppt Video Online Download
Find, Read, And Discover Reaction Coordinate Diagram E1, Such Us:
- Solved This To Me Looks Exactly Like A Sn1 Reaction Profi Chegg Com
- Dehydration Of Alcohols By E1 And E2 Elimination With Practice Problems Chemistry Steps
- Solved Based Upon The Following Energy Diagram Is This R Chegg Com
- 8 5 Elimination Reactions Chemistry Libretexts
- 3
If you re searching for Arduino Mega Diagram you've arrived at the perfect place. We have 104 images about arduino mega diagram including pictures, photos, photographs, wallpapers, and more. In such page, we additionally have number of graphics available. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, blackandwhite, transparent, etc.
A measure of freedom of motion dgo dho tdso dgdhds de are state.
Arduino mega diagram. Reaction coordinate br figure 911 reaction free energy diagram for the s n1e1 solvolysis reaction of ch 3 3cbr with ethanolthe rate limiting stepionization of the alkyl halide red curvehas the transition state of highest standard free energythe. It shows how the energy of the system changes during a chemical reaction. The heat given off or absorbed during a reaction entropy dso.
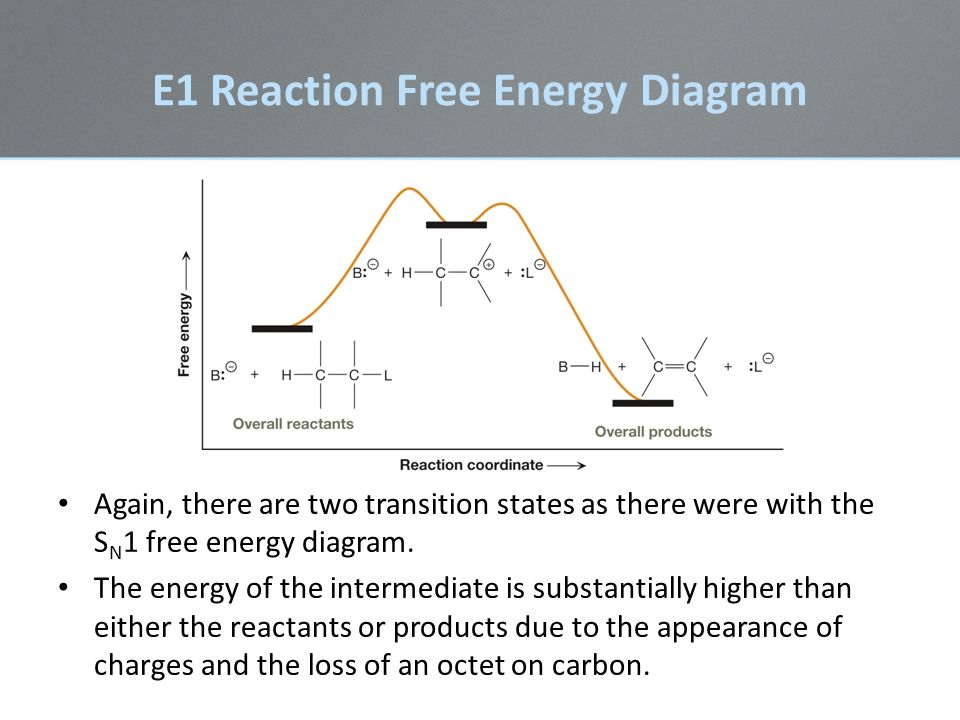
In order to determine how the rate will change we need to write the correct rate law equation for the e1 mechanism. Unlike e2 reactions the e1 reaction is not stereospecific. You may recall from general chemistry that it is often convenient to describe chemical reactions with energy diagrams.
The diagram below is called a reaction coordinate diagram. 1 complete the reaction coordinate diagram 2 answer the questions about using either water or acetone as the solvent. Consider the mechanism and.
Reaction conditions a circle the states that will be stabilized. In an energy diagram the vertical axis represents the overall energy of the reactants while the horizontal axis is the reaction coordinate tracing from left to right the progress of the reaction from starting compounds to final products. In this example b is at a lower total energy than a.
E1 is a unimolecular mechanism and the rate depends only on the concentration of the substrate r x as the loss of the leaving group is the rate determining step for this unimolecular reaction. Ron rusay a reaction coordinate energy diagram thermodynamic quantities gibbs standard free energy change dgo enthalphy dho. A base is doubled and r x stays the same.
The first step only of the reaction coordinate diagram has been shown for the e1 reaction with the starting material shown. Lets consider a general reaction where a reactant or set of reactants a is transformed into a product or set of products b. Struggling to understand catalysts or reaction coordinate diagrams or maybe trying to determine a reactions rate law from its mechanism.
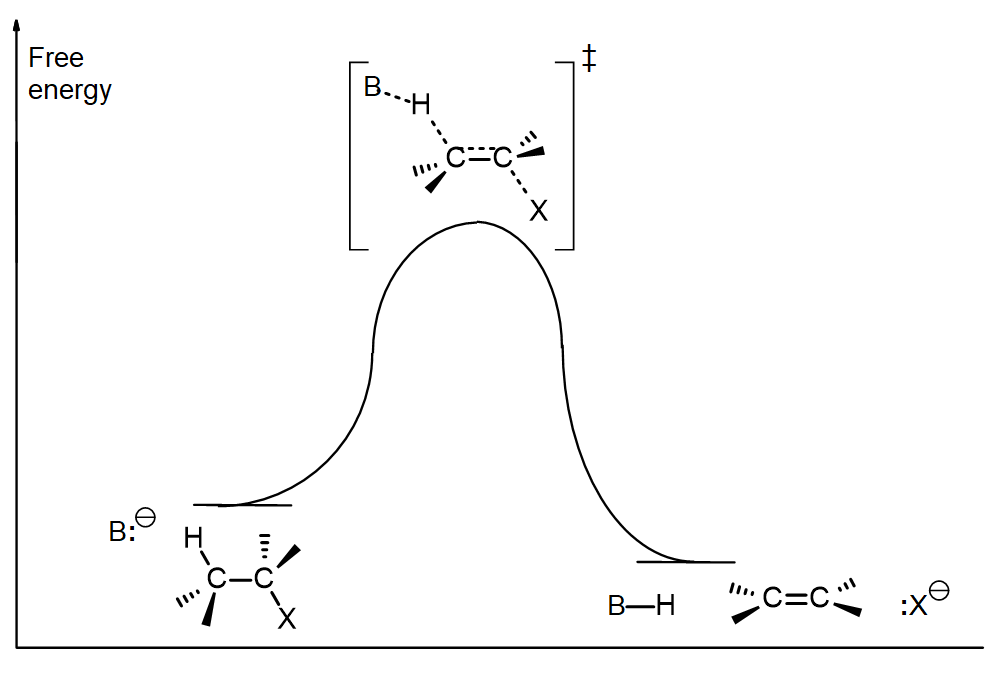
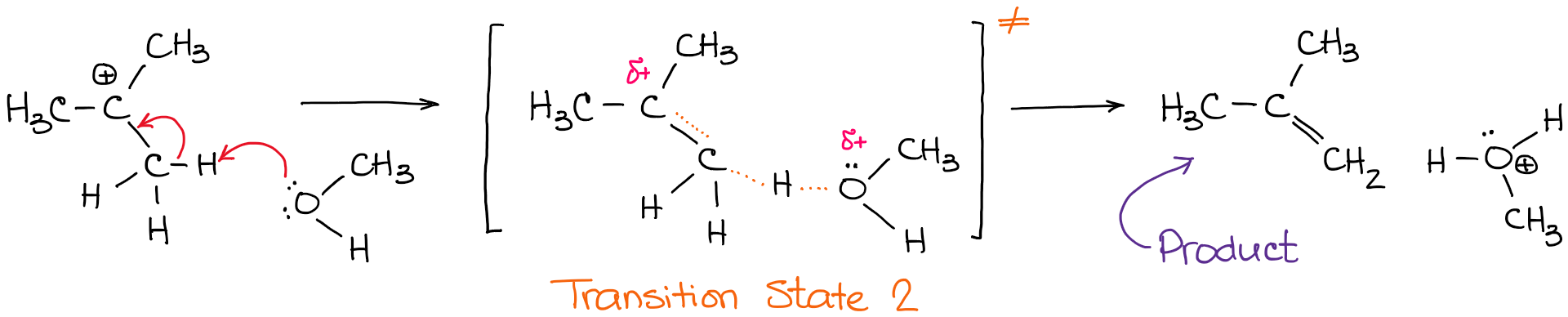
This infers that the hydrogen on the most substituted carbon is the most probable to be deprotonated thus allowing for the most substituted alkene to be formed.
Arduino Mega Diagram, Sn1 Mechanism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
- Group Work Day 3 Chapter 7 Synthesis Wiley Studocu
- Considering The Sn1 Sn2 E1 And E2 Mechanisms The E
- Sn1 Mechanism An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Arduino Mega Diagram, Energies Of Competing S N 1 And E1 Reactions In Comparison Download Scientific Diagram
- Consider The Energy Diagram For The Following Reaction A Label The Electrophile And The Nucleophile B Does The Energy Activities Chemistry Lessons Diagram
- Ch 8 Sn2 Mechanism
- Solved Which Of The Following Statements About The Free E Chegg Com
Arduino Mega Diagram, E1cb Elimination Unimolecular Conjugate Base
- 3
- Chapter8smith Reaksi Eliminasi
- Ch 8 Sn2 Mechanism
More From Arduino Mega Diagram
- Dfd Shapes Meaning
- Motor Diagram Circuit
- Bell Circuit Diagram
- Euro Trailer Plug Wiring
- Ic 74138 Pin Diagram
Incoming Search Terms:
- Https Pdfs Semanticscholar Org 7f08 60b0eee97ec0ce7510ba9d32536b585bcd0e Pdf Ic 74138 Pin Diagram,
- Elimination Reactions Ppt Download Ic 74138 Pin Diagram,
- Solved Given The Following Reaction Coordinate Diagrams Chegg Com Ic 74138 Pin Diagram,
- 2 Ic 74138 Pin Diagram,
- Dehydration Of Alcohols By E1 And E2 Elimination With Practice Problems Chemistry Steps Ic 74138 Pin Diagram,
- E1 Energy Diagram Loss Of Leaving Group Is The Rate Determining Step Energy Activities Organic Chemistry Chemistry Ic 74138 Pin Diagram,