Molecular Orbital Theory Examples, Mo Theory
- Definition Of Molecular Orbital Theory Chegg Com
- Mo Diagrams
- Heterodiatomic Molecules Mo Diagram For Co
- Sample Questions Chapter 9 Molecular Orbital Covalent Bond
- Question Bf938 Socratic
- Molecular Orbitals Molecular Orbital Theory Sparknotes
- Molecular Orbital Theory
- Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Encyclopedia Structure Number Molecule Atom Bond Order Multiple Bonds
- 9 8 M O Theory And The Period 2 Diatomic Molecules Chemistry Libretexts
- Solved Essay Which Discusses The Modern Interpretation Of Chegg Com
Find, Read, And Discover Molecular Orbital Theory Examples, Such Us:
- Chemistry 101 Molecular Orbital Theory Youtube
- Molecular Orbital Diagram Wikipedia
- Https Thinfilmsliterature Files Wordpress Com 2017 11 10 5 Molecular Orbital Theory Pdf
- Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn And9gctiec9j0hj24zdpdkfj1mgubpxdhfxodbgzojxnpyq71geqaij Usqp Cau
- Molecular Orbital Theory
If you are looking for Coronary Artery Anatomy Diagram you've arrived at the perfect place. We have 104 images about coronary artery anatomy diagram adding images, photos, photographs, wallpapers, and more. In these web page, we also have variety of graphics available. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, symbol, black and white, translucent, etc.

An Example Of A Frontier Molecular Orbital Diagram Diagram Of The Download Scientific Diagram Coronary Artery Anatomy Diagram
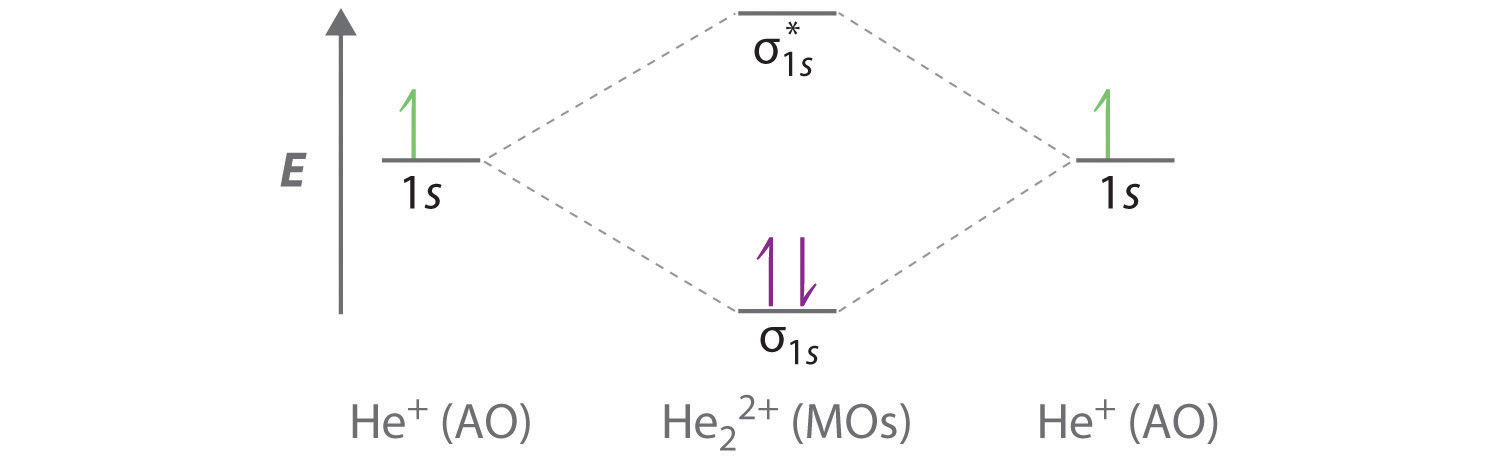
The electron density in the bonding molecular orbital in the internuclear region is high.
Coronary artery anatomy diagram. As a result the nuclei are shielded from each other and hence the repulsion is very less. These are formed by the combination of and and with part of the electron waves. Mulliken came up with molecular orbital theory to explain questions like the ones above.
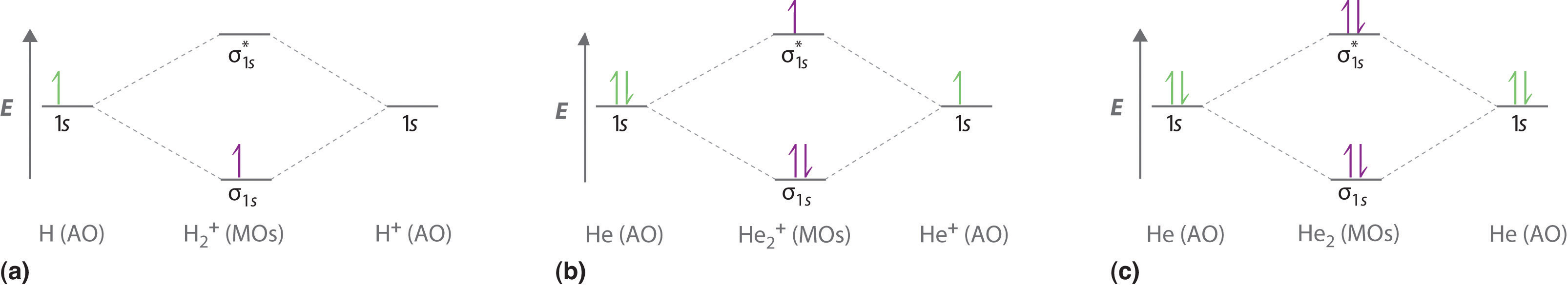
The valence bond theory fails to answer certain questions like why he 2 molecule does not exist and why o 2 is paramagnetic. Consider the h 2 molecule for example. On december 13 1910 british applied mathematician and theoretical chemist charles coulson was born.
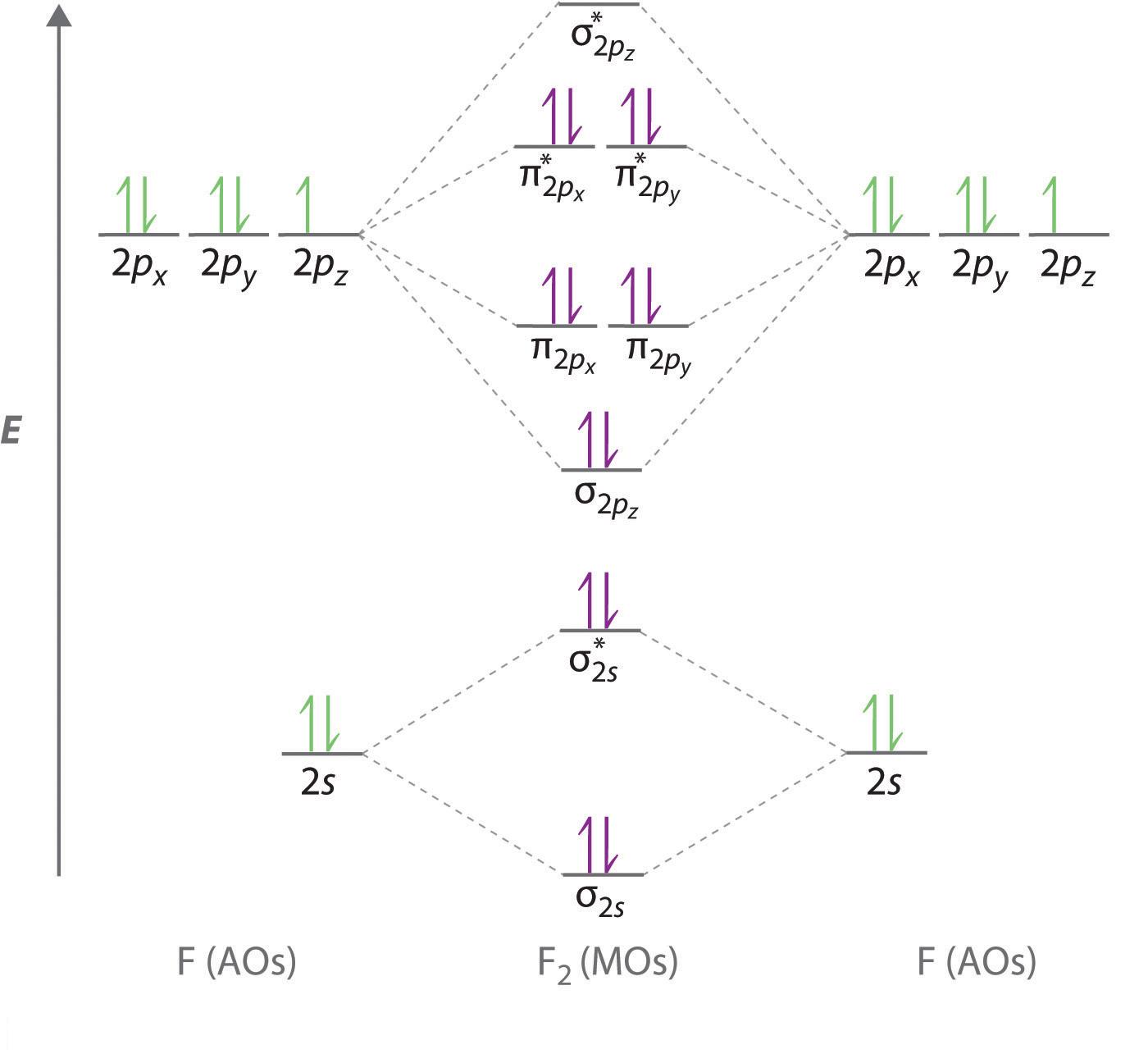
Molecular orbitals are formed by combination of atomic orbitals. Molecular orbital theory mot. Salient features of molecular orbital theroy definition 1.
These are formed by the overlap of with part. The atomic orbitals of comparable energy combine to form molecular orbitals. An electron molecular orbital is under the influence of two or more nuclei depending upon the number of atoms present in the molecule.
When we bring the 2 atoms next to each other we can make 2 mos out of the 2 1s aos. In chemistry orbital hybridisation or hybridization is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals into new hybrid orbitals with different energies shapes etc than the component atomic orbitals suitable for the pairing of electrons to form chemical bonds in valence bond theoryfor example in a carbon atom which forms four single bonds the valence shell s orbital combines with three valence. Coulson was as a pioneer of the application of the quantum theory of valency to problems of molecular structure dynamics and reactivityhe is known for the application of molecular orbital theory to chemical bonding the electronic structures of molecules and the concept of partial valency.
10 differences with examples valence bond theory is a molecular theory that is used to define the chemical bonding of atoms in a molecule. They have complex shapes. An electron in a molecular orbital is influenced by two or more nuclei depending on the number of atoms of molecule.
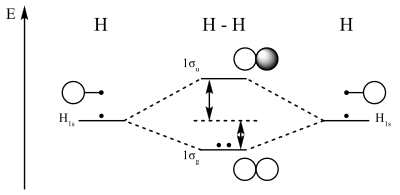
We are going to use one electron on each h atom each in a 1s orbital. Lets find the mo description of h 2. The electrons present in a molecule are present in various molecular orbitals.
Valence bond theory is based on localized bond approach in which it assumes that the electrons in a molecule occupy atomic orbitals for the individual atoms. An electron in atomic orbital is under the influence of only one positive nucleus of the atom. As always we will do a combination and a combination.
These combinations are illustrated in the figure below. As two h nuclei move toward each other the 1 s atomic orbitals of the isolated atoms gradually merge into a new molecular orbital in which the greatest electron density falls between the two nuclei. Therefore in 1932 f.
Molecular orbitals are obtained by combining the atomic orbitals on the atoms in the molecule.
Coronary Artery Anatomy Diagram, A Brief Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory Of Simple Polyatomic Molecules For Undergraduate Chemistry Students
- Molecular Orbitals Molecular Orbital Theory Sparknotes
- Molecular Orbital Theory Mot Chemistry Study Material Emedicalprep Com Emedicalprep
- Cyclobutadiene How To Build Up The Molecular Orbital Diagram
Coronary Artery Anatomy Diagram, Cyclobutadiene How To Build Up The Molecular Orbital Diagram
- Difference Between Valence Bond Theory And Molecular Orbital Theory Definition Theory Examples
- Chm1 21 Molecular Orbital Theory Collection
- Molecular Orbitals Introductory Chemistry 1st Canadian Edition
Coronary Artery Anatomy Diagram, Molecular Orbital Theory
- 9 7 Molecular Orbitals Chemistry Libretexts
- Molecular Orbitals Of The Allyl Cation Allyl Radical And Allyl Anion
- Molecular Orbitals Molecular Orbital Theory Sparknotes
More From Coronary Artery Anatomy Diagram
- Scatter Plot Definition Psychology
- Agility Brake Controller Wiring Diagram
- Zn Mg Phase Diagram
- 2008 Dodge Magnum Fuse Box Diagram
- Research Process Flowchart
Incoming Search Terms:
- What Are Some Examples Of Molecular Orbitals Socratic Research Process Flowchart,
- Mo Theory Cycloaddition Organic Chemistry Homo Lumo Conjugated System Organic Chemistry Help Research Process Flowchart,
- Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry For Majors Research Process Flowchart,
- Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn And9gcqq11kalxjqqrl5wpl1fm7 Ekklmvrzkw1t3p8wzgmiulfnp9ea Usqp Cau Research Process Flowchart,
- Molecular Orbital Theory Mot Chemistry Study Material Emedicalprep Com Emedicalprep Research Process Flowchart,
- Cyclobutadiene How To Build Up The Molecular Orbital Diagram Research Process Flowchart,