Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Complexes, Molecular Orbital Diagrams Studocu
- A Brief Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory Of Simple Polyatomic Molecules For Undergraduate Chemistry Students
- How To Understand Mo Diagrams For Cationic Octahedral Transition Metal Complexes Chemistry Stack Exchange
- Https Thinfilmsliterature Files Wordpress Com 2017 11 10 5 Molecular Orbital Theory Pdf
- Coordination Compound Ligand Field And Molecular Orbital Theories Britannica
- Figure 11 From Molecular And Electronic Structure Of Nitridochromium V Complexes With Macrocyclic Amine Ligands Semantic Scholar
- How Can I Build The Molecular Orbital Diagram Of The Complex Tetraammincopper Ii Square Planar Structure Chemistry Stack Exchange
- Molecular Orbital Diagram Of A Complex Including An Oxido Ligand Chemistry Stack Exchange
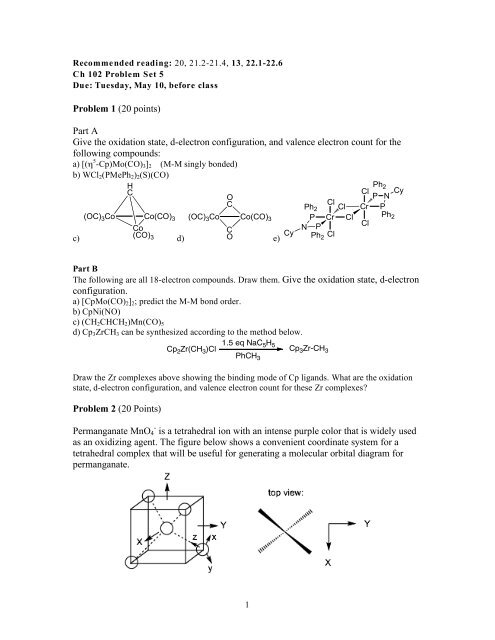
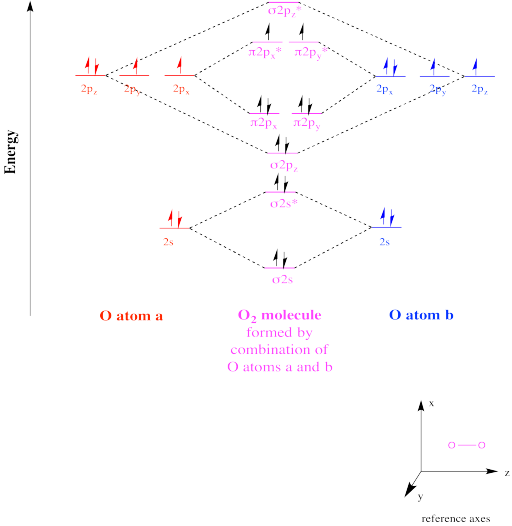
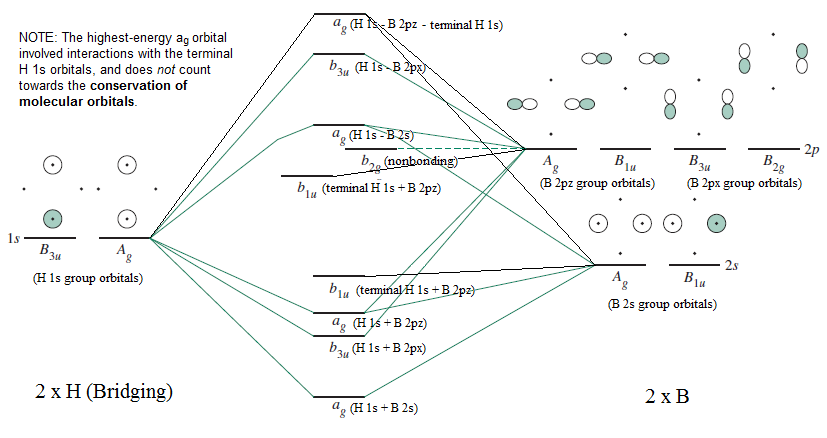
- Problem 1 20 Points Part A Give The Oxidation State Agapie Group
- For A M3x12 Metal Complex Provide A Molecular O Chegg Com
- Solved A Molecular Orbital Diagram For A Tetrahedral Tran Chegg Com
Find, Read, And Discover Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Complexes, Such Us:
- D Metal Complexes
- Ppt Molecular Orbital Theory Approach To Bonding In Transition Metal Complexes Powerpoint Presentation Id 5491714
- Https Www Chem Uci Edu Lawm 10 16 Pdf
- Http Alpha Chem Umb Edu Chemistry Ch611 Documents Mocorellationdiagrams 001 Pdf
- Introduction To Inorganic Chemistry Molecular Orbital Theory Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World
If you are searching for Control Circuit Diagram you've reached the right place. We have 104 images about control circuit diagram adding images, photos, pictures, backgrounds, and much more. In these webpage, we additionally provide number of images out there. Such as png, jpg, animated gifs, pic art, logo, black and white, translucent, etc.
In contrast to crystal field theory molecular orbital included the covalent nature of the metal ligand bond interaction.
Control circuit diagram. The levels of the molecular orbitals from the lowest energy are bonding a 1g t 1u e g non bonding t 2g anti bonding e g a 1g t 1u. This tool is very. The main features of molecular orbital theory for metal complexes are as follows.
I know i have to use the characters table the irreducible representations the rule 5 and somehow determine the energy levels of the orbitals sigma and pi. 1 st row homonuclear diatomics lecture 6 mo approach to more complex molecules and co bonding in transition metals complexes 3. I have to build the molecular orbital for the cecunh342 complex.
No metal ligand bonding bonding only lets take conh363 as an example. Distribution functions of s orbitals lecture 3 more complex wavefunctions and radial distribution functions and electron shieldin g lecture 4 lewis bonding hybridisation and molecular orbitals lecture 5 labelling mos. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories.
A molecular orbital diagram or mo diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals method in particular. With this i should be able to build the mo but i dont know how to do it. Valence bond theory and molecular.
The molecular orbital theory is highly dependent on the geometry of the complex and can successfully be used for describing octahedral complexes tetrahedral and square planar complexes. Using the lgo method one can construct a qualitative mo diagram for bonding in a ml6n. The orbital splitting between the two sets of orbitals t 2g and e g is designated as the orbital ligand field parameter d o where o stands for octahedral.
In about 15 minutes animated video the concept of molecular orbital theory mot symmetry of metal atomic orbitals in different ligand environment and mole. Gs a 1g e g t 1u six salcs with. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of molecular orbitals although the electrons involved may be redistributed among the orbitals.
These orbitals are of appropriate energy to form bonding interaction with ligands. We take six vectors pointing toward the center of a cartesian coordination system as our basis for a reducible representation of salcs gs. 73 molecular orbital approach to bonding in complexes unlike cft and lft models we will include consideration of interactions with metal ion s and p orbitals.
For example in a complex like co nh 3 6 3 18 valence electrons 6 from cobalt and 12 from ammonia occupy 9 orbitals from the bottom up and t 2g is the homo and e g the lumo. For octahedral complexes the electrons of the ligands fill all six bonding molecular orbitals whereas any electrons from the metal cation occupy the nonbonding t 2g and antibonding e g orbitals.
Control Circuit Diagram, Bonding In Octahedral And Tetrahedral Metal Complexes Molecular Orbital Theory And
- Ligand Field Theory Wikipedia
- Solved 8 A Molecular Orbital Diagram For A Tetrahedral T Chegg Com
- File Octahedral Mo Diagram Jpg Wikimedia Commons
Control Circuit Diagram, Molecular Orbital Concepts
- Transition Metal Oxo Complex Wikipedia
- Solved 2 A Molecular Orbital Diagram For A Tetrahedral Tr Chegg Com
- Molecular Orbitals For Carbon Monoxide
Control Circuit Diagram, A Brief Introduction To Molecular Orbital Theory Of Simple Polyatomic Molecules For Undergraduate Chemistry Students
- Bonding In Octahedral And Tetrahedral Metal Complexes Molecular Orbital Theory And
- Inorganic Chemistry Pages 651 700 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
- Reactivity Oxygen Reduction
More From Control Circuit Diagram
- 3 Way Switch Wiring Diagram Multiple Lights Power At Light
- Mitochondria 3d Diagram
- Flowchart For Reverse Of A Number
- Fm Demodulator Block Diagram
- Flowchart Meaning Of Shapes
Incoming Search Terms:
- Molecular Orbitals For B2h6 Flowchart Meaning Of Shapes,
- Https Www Cup Lmu De Ac Kluefers Homepage L Kc2 Literature Inverted 2016 Pdf Flowchart Meaning Of Shapes,
- File Octahedral Mo Diagram Pi Acceptor Jpg Wikimedia Commons Flowchart Meaning Of Shapes,
- Ligand Field Theory Wikipedia Flowchart Meaning Of Shapes,
- Molecular Orbital Energy Level Diagrams For A A High Spin Trigonal Download Scientific Diagram Flowchart Meaning Of Shapes,
- Lecture 26 Mo S Of Coordination Compounds Mlx X 4 6 1 Octahedral Complexes With M L S Bonds Only Consider An Example Of An Octahedral Complex Ppt Video Online Download Flowchart Meaning Of Shapes,